Driving in Dubai: Tips and requirements
Learn everything you need to know about driving in Dubai and exploring this incredible city on four wheels.
Dubai is an incredible city, and exploring it by car can be a lot of fun. Before you get behind the wheel, it is helpful to know the local rules, the documents you need, and how traffic works in this modern city. Driving in Dubai can feel easy thanks to flawless highways, digital signs, and excellent infrastructure, but there are also important differences from other countries that you should be aware of.
Dubai was built for getting around by car. Distances are often long, public transport doesn’t reach everywhere, and the heat can be intense, making driving the most convenient option for both tourists and residents. On top of that, the roads are in excellent condition and connect neighborhoods, beaches, shopping centers, and more desert-like areas quickly and easily.
If you’re thinking about driving in Dubai, we’ve got you covered. This guide will help you navigate the city with confidence, whether you’re just visiting or planning to stay longer near the Burj Khalifa. Reading this guide should be one of the first things on your to-do list.
Valid licenses for driving in Dubai
Before you drive in Dubai, the first thing to check is whether your license is valid here or if you’ll need an extra permit. Rules in the UAE vary depending on your nationality, the purpose of your visit, and how long you’ll be staying. The good news is that for most tourists, it’s usually a pretty simple process.
Valid licenses for tourists
If you’re visiting Dubai as a tourist, you can drive a rental car using your home country’s license, as long as it’s in English, has an official translation, or includes an International Driving Permit.
Most travelers get an International Driving Permit to avoid any language issues, although many rental companies accept licenses in Spanish, English, French, or German without requiring a translation. Either way, it’s a good idea to check with the agency before your trip.
Valid licenses according to country of origin
The UAE divides countries into two main groups:
- Countries whose citizens can drive WITHOUT an IDP (only with a national license): United States, Canada, United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, Japan, South Korea, South Africa, and European Union countries. In these cases, you only need to present your physical license and passport when picking up a rental car.
- Countries that require an International Driving Permit (IDP): Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Mexico, Peru, Ecuador, Paraguay, Uruguay, Bolivia, Dominican Republic, among others. If you are traveling from one of these countries, you must bring your original license + IDP to be able to drive without any issues. Agencies tend to be strict about this, especially at airport offices.
Licenses for residents (long stays)
If you plan to stay in Dubai for a longer period, whether for work, school, or relocation, you can only use your foreign license for a short time. After that, you will need a UAE driving license, and the process for getting one depends on your home country.
- If you are from the EU, UK, U.S., Canada, Australia, Japan, or South Korea, you can exchange your license without taking any tests.
- If you’re from a Latin American country such as Argentina, Mexico, Colombia, or Chile, you will need to get a UAE license from scratch, which means taking both a theory and a practical driving test.
The procedure is carried out at the Roads and Transport Authority (RTA) in Dubai.
Type of license required to drive
For private cars, the equivalent is the Light Vehicle Driving License, which lets you drive standard passenger vehicles.
Driver’s license for persons with disabilities
Dubai is an inclusive city, so people with disabilities can get a driving license as long as they meet certain requirements. There are specialized courses that cover the adaptations needed to drive safely around the city. In some cases, vehicles may also need to be modified, and drivers receive training on adapted setups.

Requirements and documentation for driving in Dubai
A valid license is only the starting point for driving in Dubai. You also need to meet a few key requirements as a driver and for your vehicle. The rules are strict, so it’s important to follow them carefully.
Minimum age for driving
You must be at least 18 to drive in Dubai, but most rental companies require drivers to be 21 or older. In some cases, depending on the type of car, the minimum age can even be 25.
Required documentation you must bring
To drive legally in Dubai, you need more than just your license and an International Driving Permit if required. You also need to carry a valid passport, a current visa or entry stamp, the rental agreement if the car is rented, the car registration documents provided by the rental company, and mandatory insurance. All documents must be physical copies since digital versions or photos are not accepted.
Mandatory insurance
Every vehicle on Dubai’s roads must have liability insurance to cover damage to others. Rental cars come with this insurance by default, but you can choose to upgrade the coverage to protect yourself from unexpected costs in case of an accident.
Vehicle conditions
Beyond all of the above, before you get in the car and hit the road, make sure the vehicle is in good mechanical condition, has a valid registration card (Mulkiya), and active insurance. You are also required to carry a spare tire, a warning triangle, and basic tools.
Rental agencies have strict controls, so you won’t have to worry about this.
Drinking and driving in Dubai
If you are driving in Dubai, remember that there is zero tolerance for alcohol. Even the smallest amount can result in serious penalties, including hefty fines, having your car taken away, and possible legal trouble.
Environmental labels and requirements
There is no environmental sticker system like in Europe, but vehicles must have working air conditioning, which is mandatory due to the climate, and be properly registered and insured in the UAE.
Stay connected while driving in Dubai
Dubai has wide avenues, multiple lanes, and roads that intersect frequently. Because of this, having a reliable internet connection is essential for using GPS, staying on route, avoiding wrong turns, and keeping in touch with your travel companions.
If you are traveling to Dubai for a short stay, a Holafly eSIM for the United Arab Emirates is all you need. It gives you unlimited data for the duration of your trip, not only in Dubai but throughout the country. Simply choose how many days you need, then activate the eSIM before boarding your flight or as soon as you land at Dubai Airport.
If you are staying in the city for a longer period, Holafly Plans is the best option. This service is designed for digital nomads, remote workers, airline crew, international students, and frequent travelers. It offers monthly plans with automatic renewal that you can cancel at any time without penalties. You also get access to a global eSIM with unlimited data or 25 GB, usable in more than 160 countries.
Important: If you are a frequent traveler and want to stay connected without worrying about expensive roaming or looking for a new SIM at every destination, Holafly’s subscription plans are for you. With a single eSIM, enjoy internet in more than 160 countries for a fixed price and no surprises on your bill. Travel without limits and connect easily and securely! 🚀🌍
Traffic rules and signage in Dubai
Driving in Dubai is quite different from what you may be used to in other destinations. The infrastructure is top tier, highways are wide, and signage is clear, but the city also has its own rules and quirks. In short, it is not something to take lightly, since traffic laws are strictly enforced and fines can be expensive.
If you don’t want the cost of living in Dubai to exceed your budget, keep reading and take note.
Direction of traffic and priorities
In Dubai, traffic flows on the right and overtaking is done on the left. If you are coming from a country where driving is on the left, renting an automatic car is a smart choice, as it helps you avoid shifting gears with your non dominant hand.
When it comes to right of way, most intersections are controlled by traffic lights, although you will also find roundabouts in less urban areas. As in most places, vehicles already circulating in the roundabout have priority.
Other situations where you need to be aware of who has the right of way include:
- When you see pedestrians at a designated crosswalk.
- When you are pulling out of a parking space (vehicles already in motion have the right of way).
- When you see children getting on or off a school bus.
- When you see emergency vehicles or military convoys.
One important tip: on major roads, plan your lane changes carefully because traffic moves quickly. The left lanes are usually for faster drivers, so if you don’t want to drive at top speed, stay in the right lanes. Always keep a safe distance of at least five seconds from the car ahead.
Speed limits in Dubai
Did you know that Dubai has some of the highest speed limits in the world? Even so, most major roads and highways are monitored by fixed speed cameras. Be careful, because going over the limit can lead to heavy fines. The cameras catch even small amounts above the allowed speed, sometimes just a few kilometers per hour.
Speed limits are clearly marked:
- 25–40 km/h in residential areas and on internal streets.
- 60–80 km/h on urban avenues.
- 100–120 km/h on highways.
Keep in mind that these are the standard speed limits, so always pay attention to the signs on each road. For example, the Sheikh Zayed Road, Dubai’s busiest highway, has a limit of 100 to 120 km/h, while Al Khail Road is limited to 100 km/h.
Use of cell phones and electronic devices
You are not allowed to use your phone while driving unless it is in a holder and used for navigation. Handling it by hand, even at a traffic light, can result in heavy fines and points on your license.
Lights, passing, and safety
Take note of these three basic rules:
- Low beams (or dipped headlights, as they are known in some countries) should be used at night or in conditions of low visibility.
- On highways, if a vehicle behind you flashes its lights, it usually indicates that it wants to overtake on the left, a common practice in the Gulf.
- When driving in desert areas or on quieter roads, make sure your car has enough fuel and check your tire pressure, as extreme heat can take a toll on both.
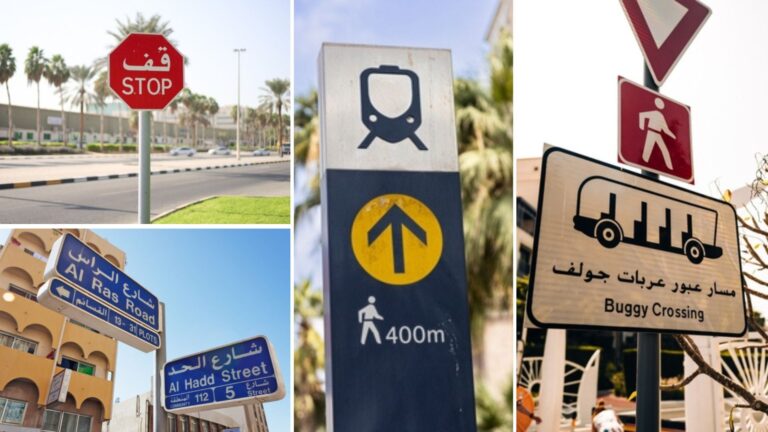

Signage in Dubai
Road signs in Dubai are some of the clearest and most modern in the Middle East. They follow UAE standards and are written in both Arabic and English, making it much easier for foreigners to navigate. You’ll also see large, well-lit signs with advance directions, which is especially helpful given the wide highways and long distances between exits.
The most common colors are:
- Green: Highways and main roads. They indicate exits, directions, and road names.
- Blue: General information, internal streets, and services (parking lots, hospitals, gas stations).
- Yellow: Warnings or temporary signs, especially in construction zones. These take priority over permanent signs.
- Red: Prohibitions (no turns, speed limits, restricted access, etc.).
The signs also use clear pictograms, much like those in Europe: large arrows, roundabout icons, camel crossing warnings in desert areas, and highly visible symbols for speed limits or speed cameras.
Something characteristic:
- Electronic signs: On highways, you will see digital panels displaying variable speed limits, traffic warnings, weather conditions, or temporary closures.
- Numbered lane indicators: Many exits show lane numbers and arrows to indicate which lane to use for each exit, helping drivers avoid sudden or risky maneuvers.
- Advance warning signs: Most highways indicate exits 500 meters, 1 kilometer, and even 2 kilometers in advance, which is essential on such wide roads.
- Signs for school zones and mosques: These indicate times and areas where you must reduce speed or avoid parking.
If you’re coming from Latin America or Europe, you’ll notice that the signs rely heavily on visual cues, but they are easy to understand and designed for drivers who don’t speak the local language. This makes driving in Dubai more intuitive than it might seem, even in areas you’re not familiar with.
Penalties and fines in Dubai
A quick reminder: take these rules seriously. Fines in Dubai are steep, and the system is designed to discourage unsafe driving. The cost depends on where and how serious the violation is, but here are some updated examples:
| Offense | Approximate fine |
| Speeding (minor) | AED 300 ($82) |
| Speeding (medium) | AED 600 ($163) |
| Speeding (serious) | AED 1,500 ($409) |
| Speeding (very serious / +60 km/h) | AED 3,000 ($817) |
| Using a cell phone while driving | AED 800 ($218) |
| Running a red light | AED 1,000 ($272) |
| Driving under the influence of alcohol | From AED 10,000 + criminal proceedings ($2,720) |
| Driving without insurance | AED 500 ($136) |
| Parking in a prohibited area | AED 200–500 ($54–$136) |
| Failure to maintain a safe distance | AED 400 ($109) |
| Dangerous overtaking | AED 600 ($163) |
| Not wearing a seatbelt | AED 400 ($109) |
| Throwing trash from a vehicle | AED 1,000 ($272) |
| Driving without a valid license | AED 500 ($136) |
Traffic peculiarities in Dubai that you should be aware of
- Traffic can be heavy during rush hour (7:30–9:30 a.m. and 5:00–7:30 p.m.).
- In areas close to the desert, sandstorms can reduce visibility.
- Many drivers change lanes more frequently than in Europe or America.
- It is common to see high-end vehicles driving at top speeds on highways.
- Taxis and delivery vehicles may stop briefly in unmarked locations; always keep your distance.
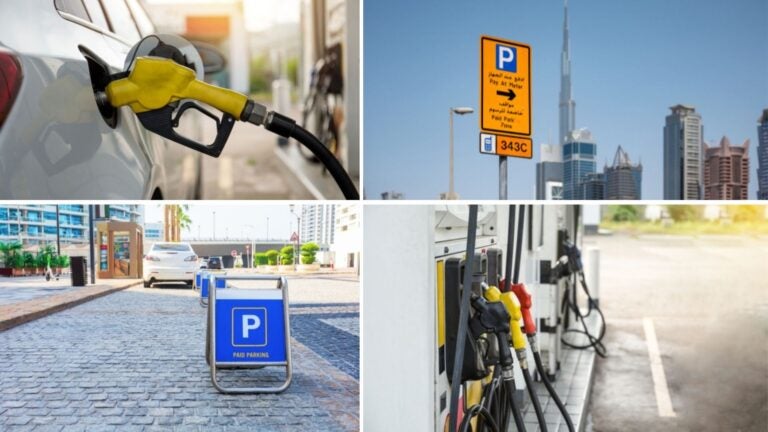
Tolls, fuel, and how to refuel in Dubai
Driving around Dubai is straightforward, but it’s useful to understand the toll system, the types of fuel available, and how to fill up without any trouble. The highways are smooth and the signs are clear, but the toll setup is unlike what you might be used to, and fuel is usually cheaper than in Europe.
Tolls in Dubai: Salik system
Dubai has a fully electronic toll system called Salik. There are no booths or barriers. When you drive through a toll gate, your license plate is scanned and the fee is charged automatically.
- Cost per crossing: AED 4 ($1.09) for each passage under a Salik gate.
- The price is fixed regardless of the time or day.
- There is no daily charge limit.
If you rent a car, the agency handles the toll system and then charges you for the tolls when you return the vehicle. It’s a good idea to check whether they add any extra processing fees.
Where are the tolls? The main Salik gates are found on Sheikh Zayed Road, Al Garhoud Bridge, the Airport Tunnel, and other key roads leading into urban areas.
Types of fuel in Dubai
Dubai has a modern network of gas stations, all clearly marked and open most of the day. The fuels available are:
- Special 95: Equivalent to 95 unleaded gasoline.
- Super 98: Equivalent to 98 octane gasoline.
- Diesel: Mainly used in large and commercial vehicles.
Prices are updated monthly by the government. For reference (recent typical values):
- Special 95: Between AED 2.70 and AED 2.90 per liter ($0.74-0.79).
- Super 98: Between AED 2.90 and AED 3.20 per liter ($0.79-0.87).
- Diesel: Between AED 3.00 and 3.30 per liter ($0.82-0.90).
As you can see, fuel in Dubai is much cheaper than in Europe or America.
How to refuel in Dubai
Refueling in Dubai is easy. Most gas stations have attendants who fill up your tank, though self-service stations are also available. Just park by the pump, let the attendant know which type of fuel you need, and pay at the counter or directly to the attendant. Payments can be made in cash, by credit or debit card, or through mobile apps.
Parking and parking areas in Dubai
Parking in Dubai is fairly straightforward, but it’s important to understand how paid zones, signage, and private lots work to avoid costly mistakes. The city is built for cars, so you’ll find parking options in almost every area, from beaches and shopping centers to residential neighborhoods and skyscraper districts.
Where you can park on public roads
Dubai has a regulated parking system in urban areas. Streets are marked with the familiar paid parking lines, known as RTA Parking Zones. Signs are clear and always show the hours, rates, and zone code.
You can park without any problems in designated areas, provided you pay the corresponding fee during active hours.
Areas where parking is NOT permitted
Although Dubai is flexible to some extent, there are places where parking is strictly prohibited:
- In front of fire hydrants or emergency exits
- On sidewalks, footpaths, or pedestrian areas
- At turning points, roundabouts, or intersections
- In bus lanes
- At entrances to mosques during prayer times
- In spaces reserved for residents or disabled persons without authorization
Illegally parked vehicles may receive automatic fines or be towed away.
Payment for parking in public areas
In Dubai, most public parking areas require payment for much of the day, especially in busy areas like Marina, Downtown, Deira, and Jumeirah. You can pay at parking meters with cash or card, use the RTA Dubai app which is the easiest option for tourists and digital nomads, or use a Nol Card, a rechargeable transport card.
- Standard areas: AED 2–4 per hour ($0.54–1.09)
- Premium areas (Downtown/Marina): AED 4–8 per hour ($1.09–2.18)
- Residential areas: Lower rates or free on certain days
Private parking lots and shopping centers
Dubai’s shopping malls have large, well-marked parking areas. The best part is that many offer free parking for the first few hours. For example, Dubai Mall is free for the initial hours, after which progressive fees apply.
Independent underground and private parking lots charge higher rates, but they are convenient in busy areas. The hourly cost is usually around AED 5 to 10 ($1.35-2.70).

Options for renting a car in Dubai
Renting a car in Dubai is one of the easiest ways to get around, especially if you plan to explore multiple neighborhoods, drive out to desert areas, or stay for an extended period. There are plenty of options, from international companies to local agencies offering very competitive rates.
The most common rental companies include Avis, Hertz, Europcar, Sixt, Enterprise, as well as local brands like Dollar, Thrifty, Fast Rent a Car, and Yelo. You can rent a car at the airport, in city offices, or even have it delivered and picked up at your hotel, as many agencies offer this service.
The most popular cars for tourists and digital nomads are compact cars, sedans, and mid-size SUVs, perfect for long drives and trips near the desert. Most vehicles are automatic, since manual transmissions are rare in the UAE.
AED 120 to 200 per day is the typical cost for an economy car, or AED 800 to 1,300 per week, depending on the season and the type of vehicle. SUVs tend to be more expensive, while monthly rentals offer reduced rates for longer stays.
If you plan to travel extensively between neighborhoods or visit the suburbs, having your own car will give you more freedom than relying on public transportation or taxis.
Final tips for driving in Dubai
Driving in Dubai can be very convenient if you understand how the city flows and what to expect from local traffic. The highways are wide and modern, but traffic often moves fast, so it’s best to drive cautiously and plan your moves ahead. A smart tip is to check your routes before heading out, as many roads have multiple lanes and exits can come up quickly if you’re not paying attention.
If you’re not used to driving in large cities, take some time to get comfortable with the pace. Stay calm and build your confidence gradually. Dubai has experienced drivers, high-end cars, and wide roads where lane changes happen frequently. Keeping a safe distance will help you avoid surprises, especially during rush hour.
It’s also wise to keep your tank topped up, especially if you plan to drive out to desert areas or on peripheral roads. Gas stations are well spaced, but distances can be longer than they look.
Also, keep in mind that the weather in Dubai can have a big impact. In the summer, extreme heat can affect tire pressure and the performance of the air conditioning, so check both before heading out on a long drive. And if there is a sandstorm, slow down and leave extra space between you and the car in front.
Finally, always use GPS without handling your phone by hand, and rely on the clear signage, which is in both Arabic and English. With a good internet connection and a bit of practice, driving in Dubai can be safe and very convenient.

Frequently asked questions about driving in Dubai
Yes, women can drive in Dubai. In fact, neighboring Saudi Arabia was the only country that used to ban women from driving, but that restriction was lifted in 2018. There are also women-only taxis, driven by female drivers.
The main highways in Dubai are:
– E11: The main artery that crosses six of the country’s seven emirates.
– Sheikh Zayed Road: Part of the central section of the E11. It is a toll highway that crosses the entire city and passes by its main points of interest.
– E311 (Sheikh Mohammed Bin Zayed Road) is a toll-free highway connecting the emirates of Sharjah, Ajman, and Umm Al Quwain with Dubai.
– E44 (Al Khail Road): This is another toll-free highway connecting Dubai with the city of Hatta and also leading to neighborhoods such as Jumeirah Lakes Towers, Deira, Ras Al Khor, and others.
– E66: Highway connecting Dubai to Al Ain from Wafi City. It runs perpendicular to the E311 and E11.
It’s generally not difficult, but traffic moves fast and the highways have multiple lanes. If you’re not used to big cities, it’s best to drive slowly at first until you get comfortable.
Yes. The main roads are well lit and visibility is generally good. In desert areas, however, it’s wise to drive more slowly because of animals or sand on the road.





 Language
Language 


















 No results found
No results found



